Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has taken the world of digital assets by storm. With the rise of blockchain technology, there has been a surge in decentralized platforms that allow users to engage in financial transactions without relying on intermediaries such as banks. However, with this newfound freedom comes a need for understanding the tax implications of these transactions.
According to TaxBit, a leading provider of crypto tax software, the IRS treats digital tokens, such as those used in DeFi, as property rather than currency. This means that each transaction involving these tokens can potentially create a taxable event. As such, individuals who engage in DeFi may have tax obligations that they need to be aware of and fulfill.
DeFi transactions can be complex and can involve various activities, such as lending, borrowing, and staking. Each of these activities can have different tax implications. For example, gains made from liquidity pooling can be subject to capital gains tax, while interest earned through lending may be treated as ordinary income.
It is important for individuals involved in DeFi to seek guidance from tax professionals who are familiar with the intricacies of this emerging field. TaxBit, for instance, has released guidance on how to navigate the tax implications of DeFi. They have also developed tools that can help individuals track and report their DeFi activities for tax purposes.
DeFi Taxes Explained
DeFi, or decentralized finance, has emerged as a rapidly growing sector in the crypto world. It offers various financial services and products, such as lending, borrowing, and earning interest, without the need for intermediaries like banks. However, navigating the tax implications of DeFi can be complex.
When it comes to taxes, traditional assets like stocks and bonds have clear guidance from the IRS. But with DeFi transactions, it’s an entirely different ball game. The IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property, which means they are subject to capital gains taxes. However, there isn’t specific guidance about DeFi taxes. This lack of clarity has left many investors unsure about their tax obligations.
There are several factors that make DeFi taxes complicated. Firstly, DeFi platforms operate in a global and decentralized manner, making it difficult to determine the jurisdiction and applicable tax laws. Secondly, the liquidity mining activities in DeFi can generate gains in digital tokens, but it’s challenging to determine the fair market value of these tokens at the time of acquisition, which is crucial for tax reporting. Additionally, certain DeFi protocols, such as lending and borrowing, involve multiple transactions, creating further complexity in calculating and reporting taxes accurately.
Fortunately, there are companies like TaxBit that specialize in helping individuals navigate the complex world of crypto taxes. TaxBit provides automated tax solutions specifically designed for cryptocurrencies and DeFi. Their software integrates seamlessly with various exchanges and platforms, allowing users to import their transaction data and generate accurate tax reports. TaxBit’s expertise and tools not only simplify the tax reporting process but also ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
It’s essential to educate yourself about DeFi taxes and seek professional assistance if needed. As the DeFi space continues to evolve and new protocols and assets are created, the tax implications will change as well. Staying informed and utilizing the tools and resources available will help ensure that you meet your tax obligations and stay on the right side of the law.
The IRS DeFi Tax
The IRS, short for the Internal Revenue Service, has found itself faced with a complex issue when it comes to taxing the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. DeFi introduces a new concept of digital assets that are not easily categorized, making it challenging for the IRS to define them under existing tax regulations.
When it comes to DeFi, the IRS treats digital tokens as property rather than currency. This means that each transaction involving cryptocurrencies, such as those in the DeFi world, may have tax implications. However, the rules surrounding these taxes are not clearly defined, leaving individuals uncertain about their tax obligations.
One source that could shed some light on the matter is TaxBit, a company that specializes in helping people navigate the complex world of cryptocurrency taxes. TaxBit has been working with the IRS to create tools and resources for individuals dealing with digital assets. This collaboration aims to ensure that tax obligations around DeFi transactions are clarified and enforced properly.
Understanding the tax implications of DeFi can be confusing, especially because each situation is unique. Different DeFi platforms and protocols may have varying tax requirements and reporting obligations. It is crucial for individuals involved in DeFi to be aware of their tax liabilities and seek professional guidance if needed. Ignoring or misunderstanding the tax implications of DeFi transactions could lead to unintended tax consequences.
Explained Gains and Liquidity in DeFi
One key aspect of DeFi that the IRS is particularly interested in is the potential for gains and liquidity. DeFi platforms allow individuals to earn interest on their holdings, provide liquidity to the market, or engage in yield farming. These activities can generate taxable income, and individuals need to report and pay taxes on these earnings.
The decentralized nature of DeFi, combined with the complex tax implications, presents a significant challenge for the IRS. As the DeFi world continues to evolve, it is crucial for regulators and individuals alike to stay informed about the tax implications of these transactions. Proper reporting and compliance with tax regulations will help ensure a smooth transition towards a regulated and transparent DeFi ecosystem.
About TaxBit
TaxBit is a world-leading provider of digital asset tax software. The company was founded in 2018 and has since released innovative solutions to assist individuals and businesses in managing their cryptocurrency taxes.
With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the increasing complexity of crypto transactions, it has become crucial for investors to have a comprehensive understanding of the tax implications. TaxBit’s software is designed to create clarity and provide guidance in these situations.
One of the key challenges in dealing with cryptocurrencies is that they are treated as property by tax agencies such as the IRS. This means that each transaction can create taxable events, and gains or losses need to be reported. Moreover, DeFi transactions can involve swapping tokens, providing liquidity, and earning interest, further complicating the tax calculation process.
TaxBit offers a range of features and tools to address these complexities. Its software can automatically calculate gains or losses based on the specific transaction details, providing accurate tax reports. It also provides guidance on how to handle different types of DeFi transactions, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
By using TaxBit, individuals and businesses can save time and effort in managing their crypto taxes. The software streamlines the process by automating calculations and generating tax forms, minimizing the risk of errors and potential audits. TaxBit’s expertise in digital asset taxes makes it a trusted source of guidance and support in navigating the complex world of DeFi and cryptocurrency taxes.
Defining Decentralized Finance and Taxation
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a term that refers to a new approach in the world of finance, where financial applications are built using blockchain technology. The main characteristic of DeFi is the elimination of intermediaries, such as traditional banks, in financial transactions. Instead, smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code, are used to facilitate transactions.
When it comes to taxation, there is still a lot of uncertainty surrounding decentralized finance. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS), the tax authority in the United States, has provided some guidance on the taxation of cryptocurrencies, but the specific tax implications of DeFi have not been clearly outlined. As such, there may be situations where the tax treatment of DeFi assets and tokens is unclear.
One of the main challenges in taxing DeFi transactions is the liquidity mining aspect. Liquidity mining involves providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of tokens. These tokens can have value and may be subject to taxation. However, the IRS has not specifically addressed the taxation of liquidity mining rewards, creating uncertainty for DeFi participants.
Furthermore, the complexity of the DeFi world can make it difficult to determine the tax implications of specific transactions. Each DeFi platform or protocol may have its own unique set of rules and mechanisms, making it challenging for taxpayers to navigate the tax landscape. Additionally, the decentralized nature of DeFi makes it difficult for tax authorities to track and monitor transactions, further complicating the tax situation.
In conclusion, while there is some guidance from the IRS on the taxation of cryptocurrencies, the tax implications of decentralized finance are still largely uncharted territory. As the world of DeFi continues to evolve, it is important for participants to stay informed and seek professional tax advice to ensure compliance with tax laws.
How DeFi Transactions Impact Taxes
DeFi transactions can have significant tax implications for individuals engaged in the digital asset space. With the rise of cryptocurrencies and the emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi), it is crucial for taxpayers to understand the tax consequences of their DeFi transactions.
However, each DeFi transaction can create a unique tax situation, and there is often limited guidance from tax authorities about how to handle these transactions. The IRS, for example, has not provided specific guidance on how to treat DeFi tokens or the various protocols used in the DeFi space.
One source that provides valuable insight into DeFi taxes is TaxBit. TaxBit is an industry-leading crypto tax software company that aims to simplify the complex tax landscape for crypto assets. According to TaxBit, cryptocurrencies acquired for investment purposes are typically considered property assets and are subject to capital gains taxes.
When it comes to DeFi transactions, there are a few key factors that taxpayers need to consider. First, the liquidity provided through various DeFi protocols can lead to taxable events. The act of providing liquidity often involves the purchase and sale of different tokens, which can trigger capital gains or losses.
Additionally, the volatility of the DeFi world can also impact the tax treatment of transactions. For example, if a cryptocurrency is swapped for another token within a short period of time, it may be considered a taxable event with potential tax implications.
In summary, DeFi transactions can have complex tax implications. Taxpayers should seek guidance from tax professionals or utilize specialized crypto tax software like TaxBit to ensure they are properly reporting their transactions and gains in accordance with applicable tax laws.
Tax Reporting Obligations for DeFi Users
Understanding and fulfilling tax reporting obligations is an essential part of being a DeFi user. DeFi, which stands for decentralized finance, has gained significant popularity in the cryptocurrency world, allowing users to access various financial services without the need for intermediaries.
When it comes to DeFi assets and gains, it is important to remember that tax obligations still apply. The IRS has been increasingly proactive about enforcing tax compliance, and this includes reporting transactions and gains related to DeFi investments.
However, tax reporting for DeFi can be complex, as each user’s situation may be different. The lack of clear guidance from the IRS about specific DeFi situations is an ongoing challenge. While there is no official tax form specifically for DeFi, it is essential to keep accurate records of transactions, gains, and losses.
To help simplify the tax reporting process, platforms like TaxBit provide tools and services specifically designed for digital asset and cryptocurrency tax reporting. TaxBit offers support for a wide range of tokens, including those used in DeFi, to ensure accurate tax calculations and reporting.
One of the complications with DeFi is the liquidity that it offers. Users can easily swap and provide liquidity for various tokens, potentially creating numerous taxable events. Understanding the tax implications of these transactions is crucial to avoid any compliance issues.
In conclusion, while tax reporting for DeFi can be complex and there is a lack of IRS guidance, it is important for DeFi users to fulfill their tax obligations. Utilizing platforms like TaxBit can help streamline the process and ensure accurate reporting of transactions and gains.
Taxes on DeFi Lending, Borrowing, and Yield Farming
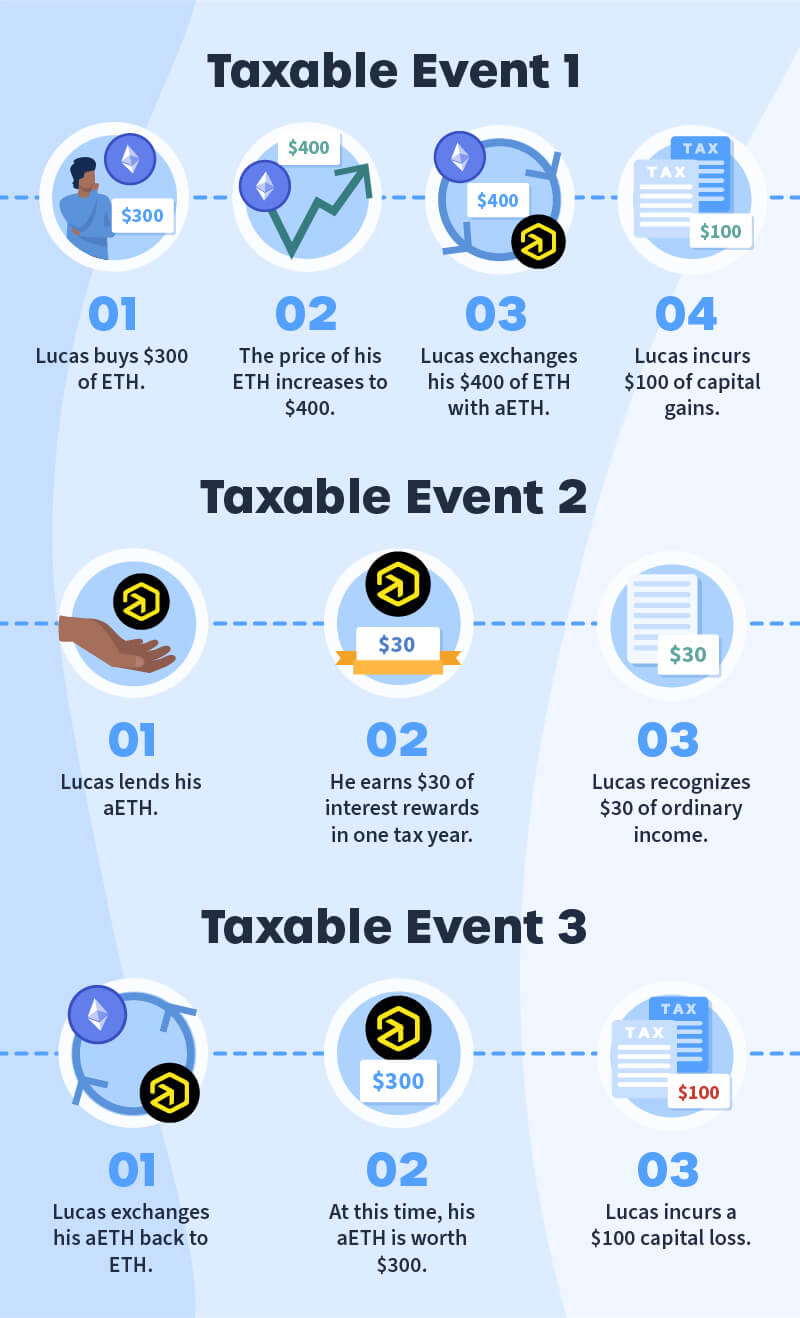
When it comes to DeFi lending, borrowing, and yield farming, there are tax implications that individuals need to be aware of. The IRS considers tokens received through these activities as taxable events, which means that each transaction must be reported and accounted for.
One of the complexities of DeFi tax situations is that different activities can create different tax obligations. For example, interest earned from lending may be classified as ordinary income, while borrowing and repaying loans may be treated as capital gains or losses. It is important to understand how each of these transactions can impact your tax liability.
While the IRS guidance on DeFi taxes is still evolving, it is essential for individuals to stay informed about the tax implications of decentralized finance activities. Failure to comply with tax regulations can lead to penalties or other legal consequences. Platforms like TaxBit can provide guidance and support in navigating the complexities of DeFi tax reporting.
Additionally, it is crucial to recognize that cryptocurrencies are considered assets for tax purposes. This means that gains or losses from DeFi activities may be subject to capital gains taxes. The value of tokens received as a yield or through liquidity mining can fluctuate, which can complicate the determination of tax liabilities.
TaxBit has released resources and guidance about taxes in the DeFi world, aiming to provide clarity on how to approach taxes for different types of decentralized finance activities. It is important for individuals to consult with tax professionals to ensure they are accurately reporting their DeFi transactions and complying with all applicable tax laws.
Capital Gains Tax on DeFi Investments
DeFi, or decentralized finance, has gained tremendous popularity in the world of cryptocurrencies. As such, the tax implications of these investments have become a major concern for many individuals. The IRS, the tax authority in the United States, has released some guidance on how these transactions should be treated for tax purposes.
Unlike traditional financial assets, cryptocurrencies are considered property for tax purposes. This means that gains made from buying, selling, or trading digital tokens are subject to capital gains tax. However, the IRS has not provided specific rules for DeFi investments.
DeFi transactions can be complex, with various interactions and transactions taking place within the decentralized ecosystem. Each transaction has the potential to create a taxable event, depending on the nature of the transaction and the resulting gains or losses.
There are several factors to consider when determining the tax implications of DeFi investments. First, the timing of the transaction is crucial. The IRS considers gains or losses to be realized when the transaction is completed, not when the funds are withdrawn from the platform.
Second, the type of asset involved in the transaction also matters. If the DeFi investment involves tokens that are categorically different from traditional cryptocurrencies, such as utility tokens or governance tokens, the tax treatment may vary.
Furthermore, the IRS’s guidance on DeFi investments is limited, leaving room for interpretation and uncertainty. In situations where the tax implications are unclear, it may be advisable to consult with a tax professional or use a specialized tax software like TaxBit.
TaxBit is a platform that offers tax software specifically designed for cryptocurrencies. It provides tools and guidance to help investors accurately calculate their tax obligations in the world of DeFi and other digital assets. With TaxBit, investors can track their transactions, generate tax reports, and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
In summary, the tax implications of DeFi investments can be complex and challenging to navigate. While the IRS has provided some guidance, there are still many unanswered questions. It is important for individuals engaged in DeFi transactions to stay informed about the latest developments and consult with tax professionals or utilize specialized tax software to ensure compliance with tax obligations.
Challenges and Considerations for DeFi Crypto Tax

When it comes to DeFi crypto tax, there are several challenges and considerations that crypto investors need to be aware of. Each decentralized finance platform operates differently, and this can create complexities when it comes to reporting gains and losses for tax purposes. The IRS has released some guidance on digital assets and taxes, but it is not entirely clear how this guidance applies to DeFi transactions.
One of the main challenges with DeFi crypto tax is the liquidity factor. DeFi platforms allow users to provide liquidity in the form of cryptocurrencies, which can generate returns in the form of transaction fees or interest. However, these returns may be considered taxable events, and it can be difficult to track and report these transactions accurately. Additionally, the value of the cryptocurrencies used as liquidity can fluctuate significantly, making it challenging to determine the gains or losses.
Another consideration for DeFi crypto tax is the classification of tokens. The IRS has defined cryptocurrencies as property, which means that they are subject to capital gains tax. However, there are many different types of tokens in the DeFi ecosystem, and not all of them may fit neatly into the category of property. This can create confusion and uncertainty when it comes to reporting and paying taxes on these assets.
Furthermore, the complex nature of DeFi transactions can make it challenging to calculate and report accurate gains and losses. DeFi platforms often involve multiple smart contracts and interactions between different protocols, which can result in a series of interconnected transactions. Tracking and documenting these transactions can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
In conclusion, DeFi crypto tax presents unique challenges and considerations for crypto investors. The lack of clear guidance from the IRS regarding DeFi transactions, the liquidity factor, the classification of tokens, and the complexity of transactions all contribute to the difficulties in accurately reporting and paying taxes on DeFi assets. It is important for crypto investors to seek professional advice and educate themselves about the tax implications of participating in DeFi.
Consult a Professional for DeFi Tax Advice
When it comes to decentralized finance (DeFi) and the tax implications involved, it is important to consult a professional for accurate guidance. The world of DeFi is entirely digital and decentralized, which means that the tax landscape can be complex and constantly evolving.
One company that specializes in crypto tax solutions is TaxBit. TaxBit offers a comprehensive platform for tracking and reporting tax obligations related to cryptocurrencies, including DeFi tokens. With TaxBit, users can easily calculate and report their gains and losses from DeFi transactions, helping them stay compliant with tax regulations.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has released some guidance about the tax treatment of cryptocurrencies, but these guidelines may not cover every situation related to DeFi. That’s why it is crucial to consult a professional who can provide personalized advice based on the specifics of your transactions and assets.
DeFi transactions can create complex tax situations, especially when it comes to liquidity mining, yield farming, and other activities that generate passive income. Some DeFi platforms reward users with tokens, and these tokens may have different tax implications depending on how they are acquired and used.
A professional tax advisor can help you navigate these complexities and ensure that you are correctly reporting your DeFi transactions. They can provide guidance on how to properly classify DeFi tokens, determine their cost basis, and calculate any taxable gains or losses.
By consulting a professional, you can have peace of mind knowing that you are fulfilling your tax obligations while taking full advantage of the benefits offered by the DeFi world.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is DeFi Crypto Tax?
DeFi Crypto Tax refers to the taxes imposed on individuals or businesses that engage in activities related to decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi involves the use of blockchain technology to create financial applications that are not controlled by any central authority. These tax implications arise from the buying, selling, lending, or borrowing of cryptocurrencies within the DeFi ecosystem.
How are DeFi taxes calculated?
DeFi taxes are typically calculated based on the gains or losses made from activities such as trading, farming, or staking cryptocurrencies within the DeFi ecosystem. The tax liability is determined by deducting the cost basis (purchase price) from the fair market value of the assets when they are sold or exchanged. It’s important to keep track of all transactions and consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate and compliant reporting.
What is TaxBit?
TaxBit is a software platform that specializes in cryptocurrency tax compliance. It provides individuals and businesses with tools and services to calculate, report, and file taxes on their cryptocurrency transactions, including those within the DeFi ecosystem. TaxBit helps users accurately determine their tax liabilities and generate necessary tax forms, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
How does the IRS handle DeFi taxes?
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies for tax purposes, including those involved in DeFi, as property rather than currency. This means that any gains or losses from cryptocurrency transactions are subject to capital gains tax. The IRS expects taxpayers to report their income from DeFi activities, including mining, trading, and lending, using Form 8949 and including it on their individual tax returns.
Video:
Crypto Taxes Explained – Beginner’s Guide 2023
Defining DeFi — Decentralized Finance



As an avid DeFi user, I have to say that understanding the tax implications of these transactions can be quite overwhelming. It’s crucial to stay compliant and fulfill our tax obligations, but it’s certainly not an easy task. I’m glad there are companies like TaxBit that can help us navigate this complex landscape and ensure we’re on the right track. Kudos to them!
Can you explain more about how gains from liquidity pooling are subject to capital gains tax in DeFi transactions?
In DeFi transactions, gains from liquidity pooling are treated as capital gains because they are considered a form of investment. When you provide liquidity to a decentralized exchange or liquidity pool, you are essentially contributing funds to a pool that allows others to trade. As a liquidity provider, you earn fees based on the transaction volume. If the value of the tokens you provided increases while they are locked in the liquidity pool, any gains you make when you withdraw your tokens will be subject to capital gains tax. It’s important to keep track of these gains and report them accurately to fulfill your tax obligations in accordance with IRS regulations. Always consult with a tax professional to ensure you understand the specific tax implications in your jurisdiction.
DeFi has revolutionized the way we transact and manage our finances. However, the tax implications can be quite confusing. It’s great to see that TaxBit is here to help us navigate through the complexities of DeFi taxes. I’ll definitely be seeking their guidance to ensure I stay compliant with my crypto tax obligations.
Very informative article! I have a question regarding the tax implications of lending on DeFi platforms. Are the interest earnings considered taxable income? Thank you!
Yes, the interest earnings from lending on DeFi platforms are considered taxable income. According to IRS regulations, any income generated from lending activities, including interest earnings, should be reported and included in your tax obligations. It is important to keep track of these earnings and consult a tax professional to ensure compliance with tax laws.
Can you provide any examples of specific tax implications for different DeFi activities? I’m interested in learning more about how lending and staking can impact my taxes.